Manganese Sulfate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Manganese(II) sulfate usually refers to the inorganic compound with the formula MnSO4·H2O. This pale pink
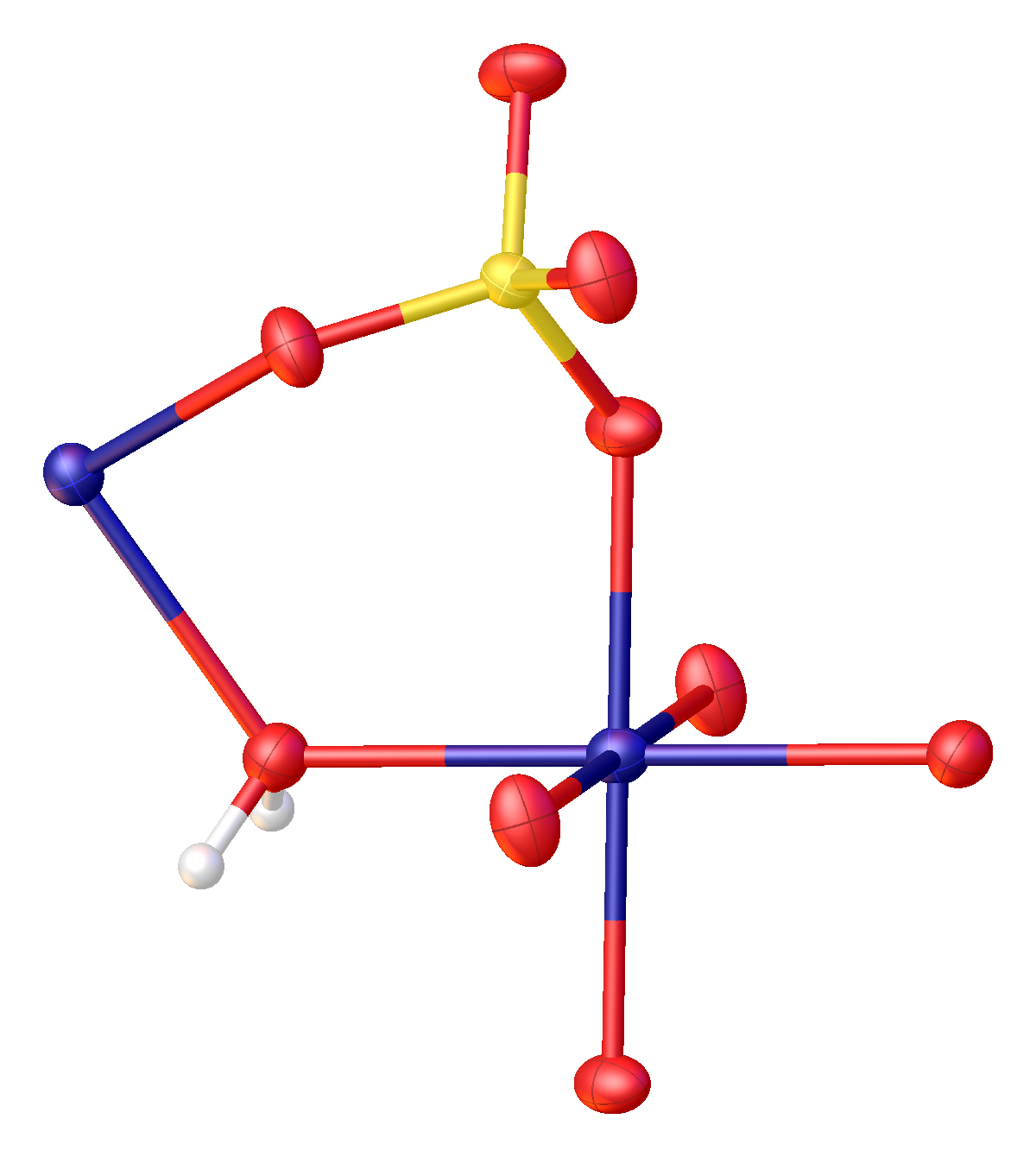 The structure of MnSO4·H2O has been determined by
The structure of MnSO4·H2O has been determined by
deliquescent
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance' ...
solid is a commercially significant manganese(II) salt. Approximately 260,000 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s of manganese(II) sulfate were produced worldwide in 2005. It is the precursor to manganese metal and many other chemical compounds
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
. Manganese-deficient soil is remediated with this salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
.
Structure
 The structure of MnSO4·H2O has been determined by
The structure of MnSO4·H2O has been determined by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
. Like many metal sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
s, manganese sulfate forms a variety of hydrates
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understo ...
: monohydrate, tetrahydrate, pentahydrate, and heptahydrate. All of these salts dissolve in water to give faintly pink solutions of the aquo complex
In chemistry, metal aquo complexes are coordination compounds containing metal ions with only water as a ligand. These complexes are the predominant species in aqueous solutions of many metal salts, such as metal nitrates, sulfates, and perchlorat ...
n(H2O)6sup>2+.
Applications and production
Typically, manganese ores are purified by their conversion to manganese(II) sulfate. Treatment of aqueous solutions of the sulfate with sodium carbonate leads to precipitation of manganese carbonate, which can becalcined
Calcination refers to thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), gener ...
to give the oxides MnO''x''. In the laboratory, manganese sulfate can be made by treating manganese dioxide with sulfur dioxide:
:MnO2 + SO2 + H2O → MnSO4(H2O)
It can also be made by mixing potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KMnO4. It is a purplish-black crystalline salt, that dissolves in water as K+ and , an intensely pink to purple solution.
Potassium permanganate is widely used in the c ...
with sodium bisulfate and hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%â ...
.
Manganese sulfate is a by-product of various industrially significant oxidations that use manganese dioxide, including the manufacture of hydroquinone
Hydroquinone, also known as benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, a derivative of benzene, having the chemical formula C6H4(OH)2. It has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a ''para' ...
and anisaldehyde
4-Anisaldehyde, or ''p''-Anisaldehyde, is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4CHO. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with an formyl and a methoxy group. It is a colorless liquid with a strong aroma. It provides sweet, floral and ...
.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis of manganese sulfate reverses the above reaction yielding manganese dioxide, which is called EMD for electrolytic manganese dioxide. Alternatively oxidation of manganese sulfate with potassium permanganate yields the so-called chemical manganese dioxide (CMD). These materials, especially EMD, are used in dry-cell batteries.Natural occurrence
Manganese(II) sulfate minerals are very rare in nature and always occur as hydrates. The monohydrate is called szmikite; tetrahydrate = ilesite; hexahydrate (the most rare) = chvaleticeite; pentahydrate = jĹŤkokuite; heptahydrate = mallardite.References
{{Sulfates Manganese(II) compounds Sulfates Deliquescent substances